
Human color vision is a fascinating process. There is no color in the external world; color is an illusion created by the interactions of billions of neurons in our brain and projected onto the outer world we see. How does the human eye experience normal color vision? The answer is with special cells in the back of the eye. Those special cells are known as rods and cones. It is cone cells that allow you to have normal color vision.
A person with normal color vision has three different color sensitive cones in their retina: red, green, and blue. Each of these three types of cones are sensitive to different wavelengths of light and help to create color perception. The unique separation and overlap work together to enable those with normal color vision to see up to 1 million different shades of colors. A person born with color blindness has their color sensitive cones positioned in such a way that there is less separation between them and an excessive overlap. This reduces the shades of colors seen and the brightness of color, compromising the perception of many colors.
This quiz will test your color acuity and perception. Can you see subtle hue distinctions that others can't? Take this color test to challenge your ability to read words in boxes of similar shades of black.
Enjoy Quizly? Upgrade to Premium for an ad-free experience and exclusive features.
Get PremiumOnly a Person Who Can See Black Well Can Read Words Quiz Questions
What word do you see?

BATS
CATS
CAST
I don't know
CARS
What word do you see?

BOAR
I don't know
BOAT
COAT
GOAT
What word do you see?

EGGS
DOGS
COGS
I don't know
BOGS
What word do you see?

DISH
FIST
I don't know
FISH
ASH
What word do you see?

NEIGH
RIGHT
I don't know
NIGHT
LIGHT
What word do you see?

BANK
DANK
DARK
BARK
I don't know
What word do you see?

DARK
BANK
DANK
I don't know
BARK
What word do you see?

SLEEP
I don't know
BLEEP
SWEET
STEEP
What word do you see?

SAT
BAT
BAD
RAT
I don't know
What word do you see?

I don't know
FOOD
FOOL
GOOD
FOOT
What word do you see?

I don't know
NOPE
HOPS
HOP
HOPE
What word do you see?

FIVE
SIRE
PINE
FIRE
I don't know
What word do you see?

I don't know
CODE
GOOD
COOK
COOL
What word do you see?

PINK
I don't know
PUNK
PINE
PIN
What word do you see?

RAT
I don't know
BAT
SAT
FAT
What word do you see?

I don't know
FIVE
LIFE
DIVE
LIVE
What word do you see?

COVE
I don't know
DOVE
DIVE
OVER
What word do you see?
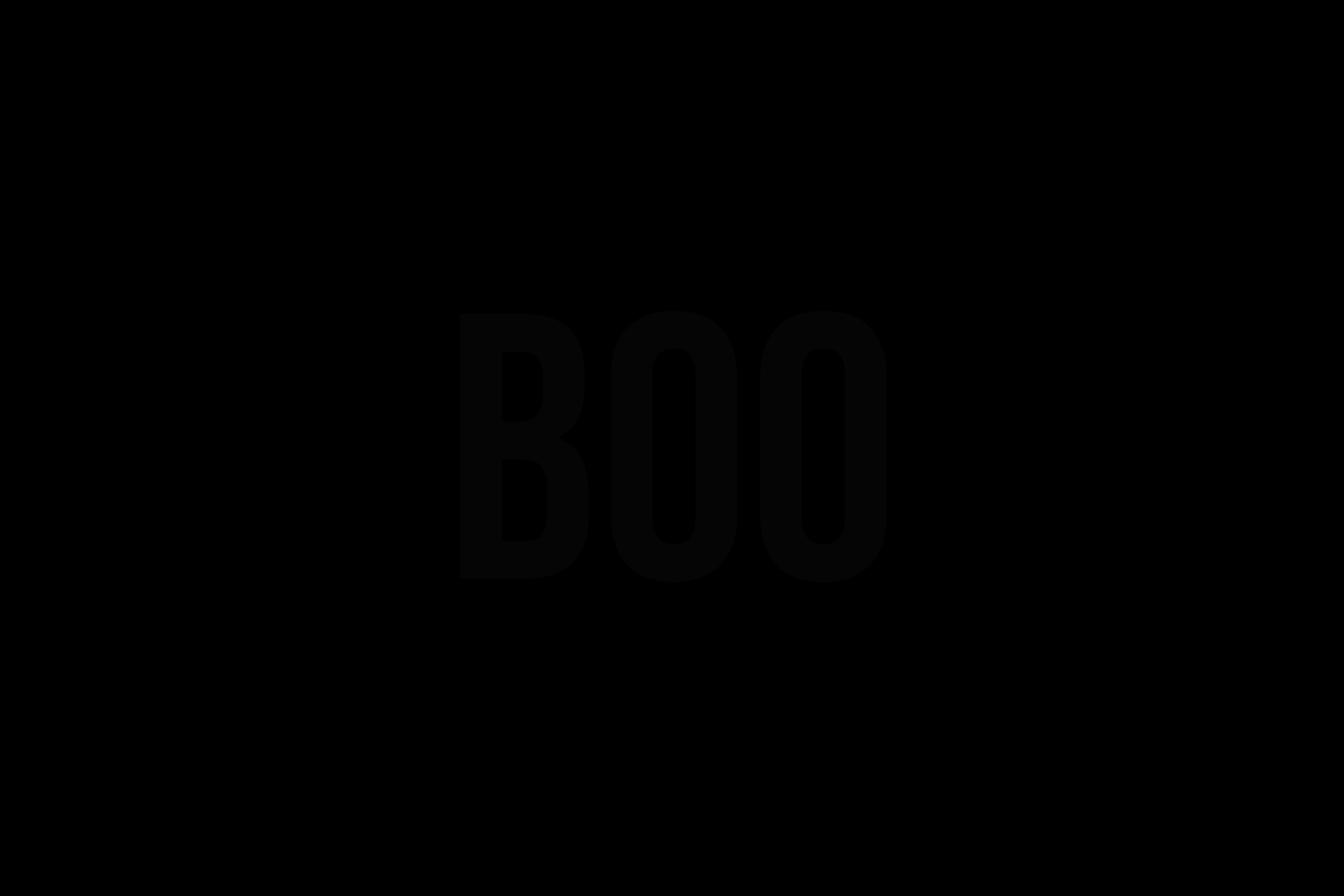
BOD
GOD
DOG
BOO
I don't know

16 Comments
This was actually a lot easier than I thought it would’ve been. 18/18
I got 18 out of 18!
Congratulations, you have perfect color vision. When it comes to seeing different color tones as well as brightness and contrast variations, you certainly have no issues.You should absolutely consider a career with Pantone.
The random smudges on my screen sure didn’t help!!!
18/18, I could read them easily
I got 15 out of 18!
Congratulations, you have perfect color vision. When it comes to seeing different color tones as well as brightness and contrast variations, you certainly have no issues.You should absolutely consider a career with Pantone.
You got: 16 out of 18!
Congratulations, you have perfect color vision. When it comes to seeing different color tones as well as brightness and contrast variations, you certainly have no issues.You should absolutely consider a career with Pantone.
18/18 perfect colour vision,not bad for almost 72, don’t need reading glasses yet either, wish ready of ny body was as good tho, lol.
15/18, all what I actually saw. no guesses.
1 / 18 5% And that was a guess the rest I couldn`t see a word.
18/18 Congratulations, you have perfect color vision. When it comes to seeing different color tones as well as brightness and contrast variations, you certainly have no issues. You should absolutely consider a career with Pantone.
I got 17 out of 18 only 2 tripped me up though
17/18! No Guessing!
That’s an awesome score! Have you tried the other color vision quizzes?
18/18 me three got them all right!!!!
15/18
Guessed a few times
Me too. Got them all though.